Are you worried about what’s really in your cookware? When it comes to keeping your meals healthy, the materials you cook with matter a lot.
Titanium cookware is becoming popular, but you might be wondering: Is titanium cookware truly non-toxic? Understanding this can help you make smarter choices for your kitchen and your health. Keep reading to discover the truth about titanium cookware and why it might be the safest option for you and your family.
Titanium Cookware Basics
Titanium cookware has gained popularity for its strength and lightweight design. Many people ask, is titanium cookware non toxic? Understanding the basics of titanium cookware helps answer this question. This section covers the essential facts about titanium’s material properties and its common uses in cookware. Knowing these details will help you decide if titanium cookware fits your kitchen needs and health preferences.
Material Properties
Titanium is a metal known for its unique qualities. It is strong yet light. Titanium does not rust or corrode easily. This makes it very durable for cooking tools. The metal is also biocompatible, meaning it rarely causes allergic reactions. These properties make titanium safe for food contact.
Key material properties of titanium include:
- High strength-to-weight ratio: Titanium is as strong as steel but much lighter.
- Corrosion resistance: It resists rust, even in salty or acidic environments.
- Non-reactive surface: Titanium does not easily react with food acids or bases.
- Biocompatibility: It is safe for human contact and often used in medical implants.
- Heat resistance: Titanium can withstand high cooking temperatures without damage.
Below is a simple comparison of titanium with other common cookware materials:
| Property | Titanium | Stainless Steel | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Light | Moderate | Very Light |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Reactivity with Food | Low | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Very High | High | Moderate |
| Heat Resistance | High | High | Moderate |
Common Uses In Cookware
Titanium’s properties make it useful in many cookware products. It appears in pure form or as part of a composite. Pure titanium cookware is rare and expensive but very durable. More often, titanium is used as a coating on nonstick pans to improve durability and safety.
Common uses of titanium in cookware include:
- Camping and backpacking gear: Titanium pots and pans are lightweight and tough, ideal for outdoor use.
- Nonstick coatings: Titanium-reinforced coatings last longer and resist scratching better than regular nonstick layers.
- Cookware with titanium cores: Some pans have a titanium core for even heat distribution and strength.
- Utensils and bakeware: Titanium is used in spatulas, baking sheets, and other kitchen tools.
Benefits of titanium cookware in everyday kitchens:
- Easy to carry and handle due to light weight.
- Long-lasting with less risk of warping or damage.
- Resistant to corrosion, so it stays safe with acidic foods.
- Non-toxic surface that does not leach harmful chemicals.
Many users prefer titanium cookware for health and durability reasons. It offers a reliable option for those wanting safe, long-term kitchen tools.

Credit: hestanculinary.com
Health Safety Of Titanium
Titanium cookware is popular for its strength and light weight. Many wonder about its safety for health. The health safety of titanium is important to understand before buying or using it in the kitchen. Titanium is known for being non-toxic and safe, but why? This section explores how titanium interacts with the body and food, proving its safety.
Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility means how well a material works with the body without causing harm. Titanium is one of the most biocompatible metals. It is used in medical implants like bone screws and dental implants. This shows it does not cause allergies or toxic reactions in most people.
Key points about titanium’s biocompatibility:
- Titanium does not release harmful ions into the body.
- It resists corrosion, so it stays stable in contact with tissues.
- It rarely causes allergic reactions or inflammation.
- The oxide layer on titanium protects it and helps the body accept it.
The table below compares titanium with other common cookware metals:
| Metal | Biocompatibility | Risk of Allergies | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | High | Low | High |
| Aluminum | Low | Moderate | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Moderate | Moderate to High | Moderate |
The excellent biocompatibility of titanium means it does not harm your body during cooking. It is safe for everyday use. This makes titanium cookware a good choice for those with sensitive skin or allergies to metals.
Reactivity With Food
Titanium is known for its very low reactivity with food. This means it does not change the taste, color, or safety of food during cooking. Many metals can react with acidic or salty foods, causing metal to leach or food to spoil. Titanium stays stable under these conditions.
Benefits of titanium’s low reactivity:
- No metal leaching: Titanium does not release harmful substances into food.
- Preserves flavor: Food tastes natural without metallic aftertaste.
- Resists stains and odors: Titanium does not absorb food smells or colors.
- Safe for all food types: Works well with acidic, salty, or alkaline foods.
The following points highlight why titanium is preferred in cookware:
- Titanium’s oxide layer acts as a protective barrier.
- This layer prevents chemical reactions with food.
- It keeps cookware surface smooth and non-porous.
- No toxic substances enter the food during cooking.
Here is a comparison of reactivity between titanium and other metals:
| Metal | Reactivity with Acidic Food | Reactivity with Salty Food | Risk of Metal Leaching |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Very Low | Very Low | None |
| Aluminum | High | Moderate | Possible |
| Copper | Moderate | Moderate | Possible |
In summary, titanium cookware is safe for health. It does not react with food or release toxins. Its strong protective layer keeps food pure and healthy.
Comparing Titanium With Other Materials
Titanium cookware is well-known for its durability and light weight. Many people wonder if it is truly non-toxic compared to other common cookware materials. Understanding how titanium compares to materials like aluminum, stainless steel, and cast iron helps to see its safety and health benefits clearly. Each material has unique properties that affect cooking and health differently. This section breaks down those differences to guide better choices.
Aluminum And Non-stick Coatings
Aluminum is popular in kitchens because it heats up quickly and evenly. However, pure aluminum can react with acidic foods, causing a metallic taste and potential health concerns. To avoid this, many aluminum pans have non-stick coatings. These coatings often contain chemicals like PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene).
Concerns with aluminum and non-stick coatings:
- Aluminum may leach into food, especially with acidic ingredients.
- Non-stick coatings can release harmful fumes if overheated above 500°F (260°C).
- Coatings can scratch or wear off, exposing the aluminum underneath.
Titanium cookware often has a hard, non-toxic surface without chemical coatings. This makes it safer for high-heat cooking and reduces the risk of harmful substances entering food.
| Feature | Aluminum with Non-Stick | Titanium Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Reactivity | Can react with acidic foods | Non-reactive |
| Surface Coating | Often PTFE or ceramic coatings | Usually hard anodized or pure titanium surface |
| Heat Resistance | Risk of fumes if overheated | High heat safe |
| Durability | Coatings may wear off | Highly durable, scratch resistant |
Stainless Steel And Cast Iron
Stainless steel and cast iron are classic cookware choices. Both are generally safe and non-toxic but differ in care and cooking style. Stainless steel does not react with food and is easy to clean. Cast iron adds iron to food, which can be beneficial or unwanted depending on health needs.
Key points about stainless steel:
- Non-reactive and safe for all foods.
- Can sometimes release small amounts of nickel or chromium.
- Requires proper heating to avoid food sticking.
Key points about cast iron:
- Provides natural non-stick surface after seasoning.
- Can leach iron, which may help or harm depending on individual health.
- Heavy and requires regular maintenance to prevent rust.
Titanium cookware combines benefits from both types. It is lightweight like stainless steel and does not need seasoning like cast iron. Its non-toxic nature and resistance to corrosion make it a strong alternative for safe cooking.
| Material | Reactivity | Weight | Maintenance | Health Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Non-reactive | Moderate | Low | May release nickel/chromium |
| Cast Iron | Reacts by adding iron | Heavy | High (seasoning needed) | Iron leaching can be good or bad |
| Titanium | Non-reactive | Lightweight | Low (easy to clean) | Non-toxic, no metal leaching |

Credit: aialb-sb.org
Potential Risks And Concerns
Titanium cookware is popular for its strength and light weight. Many people choose it because it is often labeled as non-toxic. Despite these benefits, some risks and concerns exist. Understanding these issues helps make safer choices for your kitchen. Below are key points about potential problems related to titanium cookware.
Manufacturing Impurities
Pure titanium is safe and non-reactive. However, the manufacturing process can introduce impurities. These impurities may affect the cookware’s safety and quality.
Common impurities include:
- Heavy metals: Small amounts of aluminum, vanadium, or iron may remain.
- Alloys: Some titanium cookware uses titanium alloys, not pure titanium.
- Trace chemicals: Residues from processing chemicals might be present.
These impurities can cause:
- Metal leaching during cooking
- Possible allergic reactions
- Reduced corrosion resistance
Check the table below for impurity types and their possible effects:
| Impurity Type | Source | Possible Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Alloying process | May leach into food; linked to health concerns |
| Vanadium | Alloy component | Potential toxicity in large amounts |
| Iron | Production residue | Can cause rusting and affect taste |
| Chemical residues | Manufacturing cleaning agents | Possible contamination if not cleaned properly |
Choosing cookware labeled as 100% pure titanium and from trusted brands reduces impurity risks. Always follow cleaning instructions to remove manufacturing residues before first use.
Surface Coating Issues
Many titanium cookware pieces have surface coatings to improve non-stick properties. These coatings may bring potential risks depending on their type and quality.
Common coating types:
- Non-stick ceramic coating
- PTFE (Teflon) coating
- Hard-anodized surface
Potential concerns with coatings:
- Peeling or chipping: Damaged coatings can mix with food and cause ingestion.
- Toxic fumes: Overheating some coatings releases harmful gases.
- Short lifespan: Coatings may wear out faster than the titanium base.
Important tips to avoid coating problems:
- Use low to medium heat to prevent damage.
- Avoid metal utensils that scratch the surface.
- Replace cookware if coating shows signs of wear.
Here is a quick look at coating risks in a table:
| Coating Type | Risk | Safety Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Chipping and wear | Use wooden or silicone utensils |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Releases fumes if overheated | Cook on low heat, avoid overheating |
| Hard-anodized | Less non-stick; can scratch | Use gentle cleaning methods |
Choosing titanium cookware without coatings or with high-quality, non-toxic coatings reduces health risks. Proper care extends the life and safety of your cookware.
Care And Maintenance Tips
Titanium cookware is popular for its non-toxic and durable qualities. To keep it safe and long-lasting, proper care and maintenance are key. Knowing how to clean and protect titanium cookware helps maintain its quality and prevents damage. This section offers simple tips to care for your titanium pots and pans so they stay in great shape for years.
Cleaning Guidelines
Cleaning titanium cookware is easy but requires some attention to avoid scratches and stains. Always let the cookware cool before washing it. Sudden temperature changes can warp the metal.
- Use warm water and mild dish soap for regular cleaning.
- A soft sponge or cloth works best to prevent scratching the surface.
- Avoid steel wool or abrasive scrubbers as they can damage the finish.
- For stuck-on food, soak the cookware in warm soapy water for 15-20 minutes before gently scrubbing.
- Dry the cookware immediately with a soft towel to prevent water spots.
For tougher stains or discoloration, try this simple natural solution:
| Ingredient | Amount | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Baking soda | 2 tablespoons | Mix with water to form a paste, apply on stains, and scrub gently. |
| White vinegar | 1 cup | Soak the cookware for 10 minutes, then rinse and dry. |
Regular cleaning after each use keeps titanium cookware safe and non-toxic for cooking. Avoid harsh chemicals or bleach, as they can damage the surface and reduce the cookware’s lifespan.
Avoiding Damage
Protecting titanium cookware from damage ensures it remains non-toxic and functional. Avoid sudden temperature changes like putting hot cookware into cold water. This can cause warping or cracks.
Use wooden, silicone, or plastic utensils to prevent scratching. Metal utensils may leave marks or damage the titanium surface.
- Do not use high heat settings for long periods; titanium heats quickly and retains heat well.
- Avoid stacking titanium cookware without protection between pieces; use a cloth or paper towel.
- Store cookware in a dry place to prevent moisture buildup and corrosion.
- Inspect cookware regularly for dents, cracks, or loose handles and fix issues promptly.
Handling titanium cookware gently keeps it safe and non-toxic. Proper use and storage extend its life and maintain cooking quality. These simple steps prevent damage and ensure the cookware stays a healthy choice for your kitchen.
Choosing Safe Titanium Cookware
Titanium cookware is known for its durability and lightweight design. Many people choose it because it is considered safer and non toxic compared to other materials. However, not all titanium cookware is made the same way. Choosing safe titanium cookware means paying attention to quality and safety standards. This helps avoid harmful chemicals or coatings that may release toxins when heated. Selecting the right product ensures a healthier cooking experience and peace of mind.
Certifications To Look For
Certifications guarantee that titanium cookware meets safety and quality standards. These marks show the product has passed tests for harmful substances and food safety. Look for the following certifications:
- FDA Approval: Confirms the cookware is safe for food contact.
- LFGB Certification: A strict European test for food safety and chemical limits.
- RoHS Compliance: Ensures no dangerous heavy metals like lead or cadmium.
- ISO Standards: Indicates high quality and consistent manufacturing processes.
Here is a quick comparison of these certifications:
| Certification | Focus Area | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| FDA Approval | Food safety in the USA | High |
| LFGB Certification | European food contact safety | High |
| RoHS Compliance | Limits hazardous substances | Medium |
| ISO Standards | Quality management | Medium |
Choosing titanium cookware with these certifications helps avoid toxic coatings and unsafe materials. Always check product labels and packaging for these marks before buying. This reduces the risk of exposure to harmful chemicals during cooking.
Trusted Brands
Brands with a strong reputation often provide safer titanium cookware. They invest in quality materials and follow strict manufacturing rules. Trusted brands usually offer detailed product information and certification proof. This transparency helps buyers make safe choices.
Some tips for choosing trusted brands:
- Research customer reviews and ratings online.
- Check if the brand offers warranty or money-back guarantees.
- Look for brands specializing in titanium or non-toxic cookware.
- Verify if the brand discloses material sourcing and testing processes.
Here is a sample list of qualities found in trusted brands:
| Quality | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Transparency | Clear details about titanium purity and coatings |
| Certifications | Verified safety and quality marks on products |
| Customer Support | Responsive help and warranty services |
| Positive Feedback | High ratings and good reviews from users |
Picking titanium cookware from well-known, trusted brands lowers risks of toxicity. It ensures the product is tested, safe, and built to last.
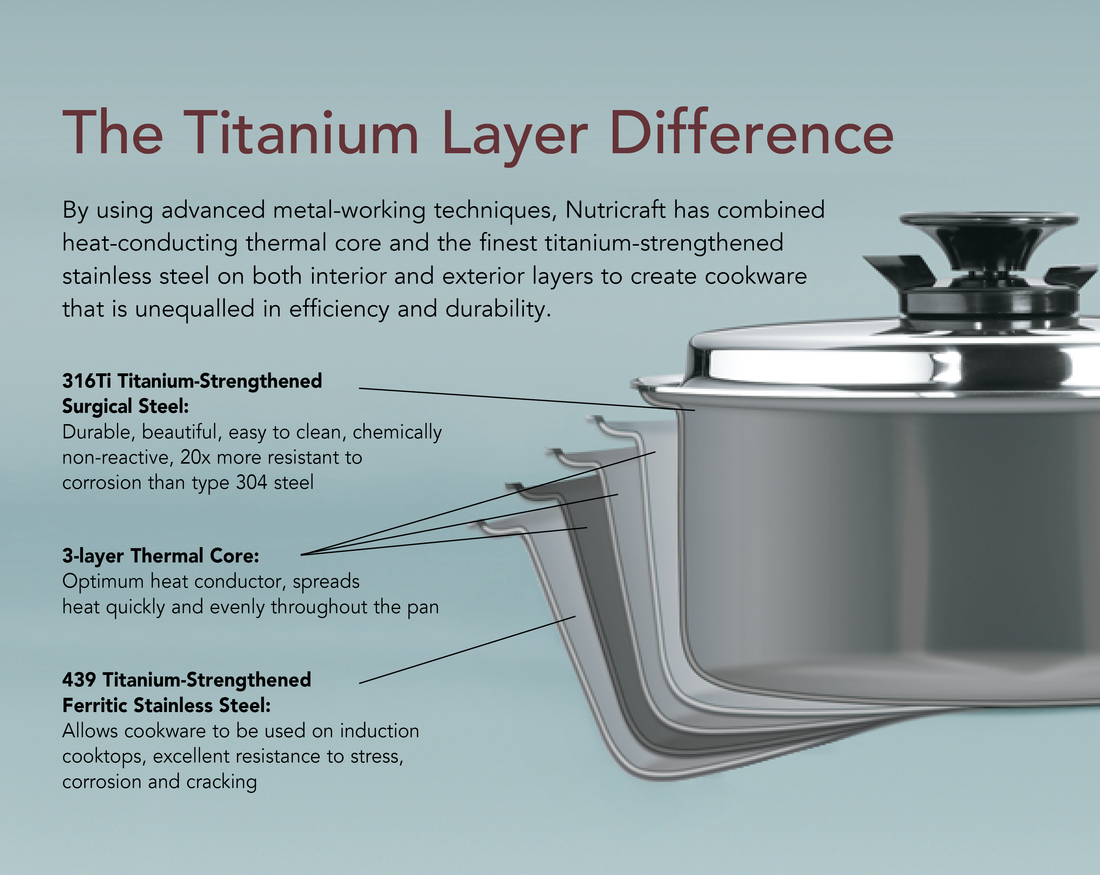
Credit: nutricraftcookware.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Titanium Cookware Completely Non Toxic To Use?
Yes, titanium cookware is non toxic and safe for cooking. It does not leach harmful chemicals into food, making it ideal for health-conscious users.
How Does Titanium Cookware Compare To Other Materials?
Titanium is lighter, more durable, and non reactive compared to aluminum or non-stick cookware. It resists corrosion and doesn’t release toxins.
Can Titanium Cookware Cause Allergic Reactions?
Titanium is hypoallergenic and rarely causes allergic reactions. It is suitable for people with metal sensitivities or allergies.
Is Titanium Cookware Safe At High Cooking Temperatures?
Yes, titanium cookware maintains safety at high temperatures. It does not release toxic fumes or degrade, unlike some coated pans.
Conclusion
Titanium cookware offers a safe choice for everyday cooking. It does not release harmful chemicals or toxins. Many people prefer it for healthy meals and durability. Easy to clean and light to handle, it suits busy kitchens well. Choosing non-toxic cookware helps protect your family’s health.
Titanium stands out as a strong, reliable option. Trust in cookware that supports safe and tasty food. Simple, safe, and long-lasting—titanium meets many kitchen needs.

Hello, This is Annie Walker, a 38-year-old blogger, founder, and editor of Cookware Guider from NY, USA. I am a cookware fanatic and passionate cooker. I love to cook with different types of cooking appliances (example: all types of cookware, rice cookers, slow cookers, etc) almost every day in my kitchen. I love to share my experience with my readers in my blog. Also, I enjoy helping people to solve their problems through my website. You can follow me on Twitter & Pinterest. To know details about my blog please check the about us page.
